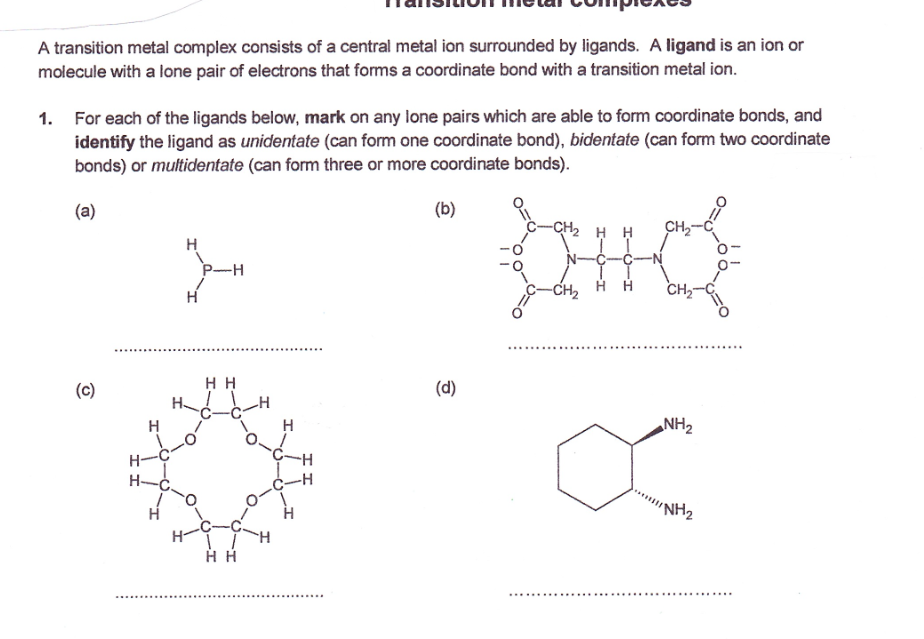
In chemistry, a transition metal chloride complex is a coordination complex that consists of a transition metal coordinated to one or more chloride ligand. The class of complexes is extensive.
Bonding
Halides are X-type ligands in coordination chemistry. They are both σ- and π-donors. Chloride is commonly found as both a terminal ligand and a bridging ligand. The halide ligands are weak field ligands. Due to a smaller crystal field splitting energy, the homoleptic halide complexes of the first transition series are all high spin. Only [CrCl6]3− is exchange inert.
Homoleptic metal halide complexes are known with several stoichiometries, but the main ones are the hexahalometallates and the tetrahalometallates. The hexahalides adopt octahedral coordination geometry, whereas the tetrahalides are usually tetrahedral. Square planar tetrahalides are known for Pd(II), Pt(II), and Au(III). Examples with 2- and 3-coordination are common for Au(I), Cu(I), and Ag(I).
Due to the presence of filled pπ orbitals, halide ligands on transition metals are able to reinforce π-backbonding onto a π-acid. They are also known to labilize cis-ligands.
Homoleptic complexes
Homoleptic complexes (complexes with only chloride ligands) are often common reagents. Almost all examples are anions.
1st row
2nd row
Some homoleptic complexes of the second row transition metals feature metal-metal bonds.
3rd row
Heteroleptic complexes
Heteroleptic complexes containing chloride are numerous. Most hydrated metal halides are members of this class. Hexamminecobalt(III) chloride and Cisplatin (cis-Pt(NH3)2Cl2) are prominent examples of metal-ammine-chlorides.
Hydrates
As indicated in the table below, many hydrates of metal chlorides are molecular complexes. These compounds are often important commercial sources of transition metal chlorides. Several hydrated metal chlorides are not molecular and thus are not included in this tabulation. For example the dihydrates of manganese(II) chloride, nickel(II) chloride, copper(II) chloride, iron(II) chloride, and cobalt(II) chloride are coordination polymers.
Adducts
Metal chlorides form adducts with ethers to give transition metal ether complexes.
References